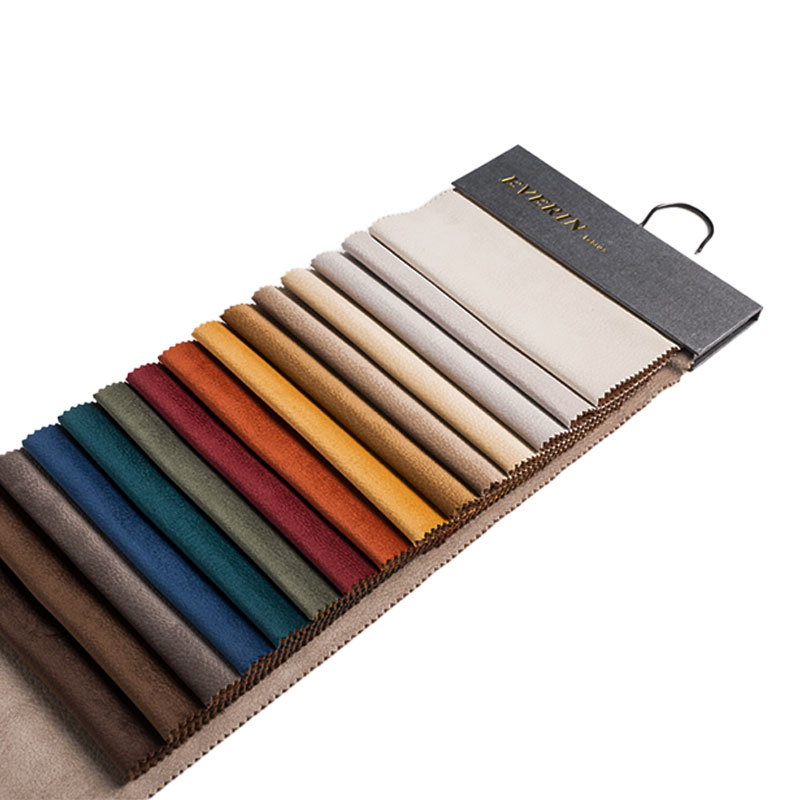
Holland Velvet and ordinary velvet are both velvet materials, but they may differ in production process, materials, etc., which may affect durability and color fastness. The following is a comparative analysis of their durability and color fastness:
AR331 220gsm Upholstery Holland Velvet Embossing Plain Color Sofa Fabric
Durability
Holland Velvet
Fabric Strength: Holland velvet usually uses high-quality fiber materials, such as long-staple cotton or high-quality silk. The strength of these fibers is inherently high, making the fabric of Holland velvet relatively tough. For example, the fiber length of long-staple cotton is longer, and the fibers are closely interwoven, which can withstand greater tension and friction.
Production process: Its production process is relatively delicate, including complex weaving and shearing processes. During the weaving process, the fibers are closely arranged and fixed, making the structure of the fabric more stable. This delicate process can reduce the deformation and wear of the fabric during use, thereby improving durability.
Abrasion resistance: The surface fluff of Holland velvet has been specially treated, and the length and density of the fluff are moderate. In daily use, such as sofa covers, curtains, etc., it can resist a certain degree of friction and scratching. Even after multiple frictions, the fluff is not easy to fall off or deform, maintaining a good appearance and feel.
Wrinkle resistance: Due to the advantages of its fiber quality and production process, Dutch velvet is also relatively wrinkle-resistant. During use, even if it is subjected to a certain amount of pressure or folding, it can quickly restore flatness, reduce the generation of wrinkles, and extend its service life.
Ordinary velvet
Fabric strength: The fiber materials of ordinary velvet may be relatively diverse, and the quality is also uneven. Some ordinary velvets may use shorter fibers, such as short-staple cotton or artificial fibers. The strength and toughness of these fibers are relatively low, resulting in the overall strength of the fabric being not as good as that of Dutch velvet. For example, the fiber length of short-staple cotton is shorter, the connection between the fibers is not tight enough, and it is easier to break when subjected to external forces.
Production process: The production process of ordinary velvet is relatively simple, and it may not be as fine as Dutch velvet during the weaving and shearing process. This makes the structure of the fabric relatively loose, prone to deformation and wear. For example, during the shearing process, if the length and density of the pile are not accurately controlled, the pile may be too long or too short, affecting the wear resistance and appearance of the fabric.
Wear resistance: The wear resistance of ordinary velvet is relatively weak. During use, the pile is easy to fall off, especially in places with frequent friction, such as sofa armrests, curtain edges, etc. The shedding of the pile will cause alopecia on the surface of the fabric, affecting the appearance and reducing the service life.
Wrinkle resistance: Ordinary velvet is also not as wrinkle-resistant as Dutch velvet. Due to the limitations of fiber quality and production process, ordinary velvet is prone to wrinkles after being pressed or folded, and it recovers slowly. These wrinkles affect the appearance and use of the fabric and shorten its service life.
Color fastness
Holland Velvet
Dyeing process: Dutch velvet usually uses advanced dyeing technology, which can make the dye penetrate evenly into the fiber. This dyeing process can ensure the stability and durability of the color. For example, some Dutch velvets are dyed with reactive dyes, which can form a strong chemical bond between the reactive dye and the fiber, making the color not easy to fall off.
Color stability: Dutch velvet has good color stability under conditions such as light, friction, and washing. Even during long-term use, the color is not easy to fade or change. For example, under direct sunlight, Dutch velvet can resist the erosion of ultraviolet rays and maintain its original bright color.
Washing color fastness: Dutch velvet has high washing color fastness. In the normal washing process, even with conventional detergents and washing methods, the color is not easy to be washed off or faded. This is because its dyeing process and fiber quality advantages enable the color to be firmly attached to the fiber.
Ordinary velvet
Dyeing process: The dyeing process of ordinary velvet may be relatively simple, and the penetration and fixation of the dye may not be sufficient. This makes the color stability relatively poor, and it is easy to have color difference or fading. For example, some ordinary velvets may be dyed with direct dyes, and the binding force between direct dyes and fibers is weak, and it is easy to be affected by external factors and fade during use.
Color stability: Ordinary velvet is not as color stable as Dutch velvet under conditions such as light, friction, and washing. The color is easy to fade or change color under direct sunlight or frequent friction. For example, some ordinary velvets will become dull and lose their original brightness after being used for a period of time.
Washing color fastness: The washing color fastness of ordinary velvet is relatively weak. During the washing process, the color is easily washed off or faded, especially when using detergents containing bleaching ingredients, the fading phenomenon is more obvious. This is because the color adhesion is not strong enough due to the limitations of its dyeing process and fiber quality.
 English
English Español
Español








